

“It came at 2 a.m., and it came on low tide, but it was pretty substantial,” Suleimani said. Until now, it has been widely assumed that the tsunami did not hit Anchorage after the 1964 quake, but this research also proved that’s not the case. The quake generated the most destructive tsunami in North America, which killed more than 100 people.
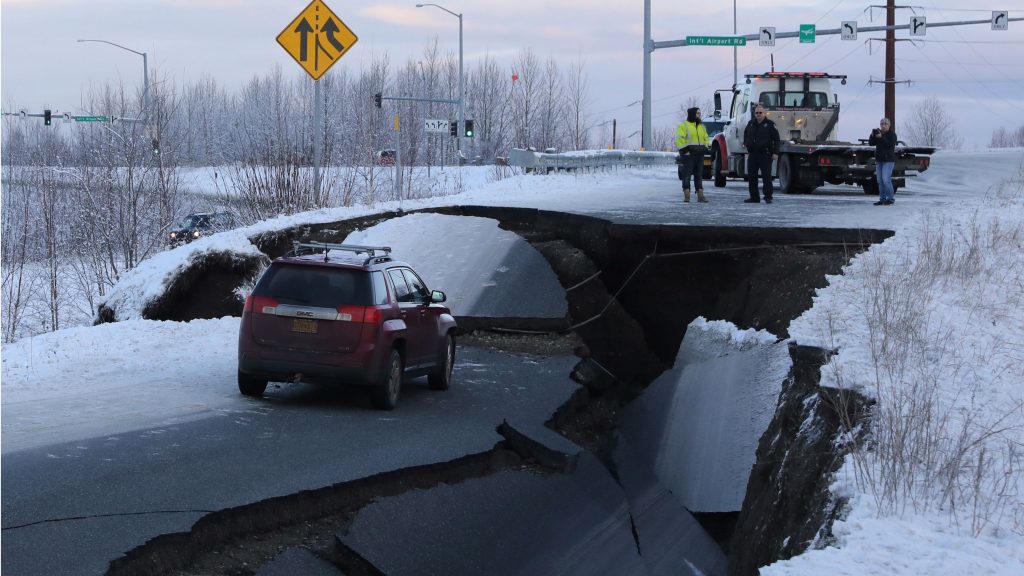

Army Engineer District in Alaska (1867-1992), Lisa Mighetto and Carla Homstad, 1997.The areas just west and east of Anchorage have had real-life examples of megathrust earthquakes, including the 1964 Great Alaska Earthquake, which was the largest quake to ever hit the Northern Hemisphere. Geological Survey, and NOAA/NGDC.Įngineering in the Far North - A History of the U.S.
#Alaska quake center code#
To the earthquake victims the code name for the relief effort, "Operation Helping Hand," seemed apt.Įarth Science Photographs from the U.S.
Once again the Corps had moved quickly and efficiently to assist people in desperate circumstances. In addition, the Alaska District channeled most of the restoration work to hard-hit local businesses, providing employment to residents whose livelihoods had been disrupted.Īltogether the Corps spent more than $110 million on salvage, rescue, and rehabilitation operations in Alaska. Racing against the calendar, the Corps managed to complete most important repairs before the Alaskan winter arrived. As one bulldozer operator reported, "It took us twelve hours to cut through the biggest slide, and when we got through there was another just ahead." In Anchorage alone, reconstruction expenditures averaged $1 million a month for the first year after the disaster. Merely clearing roadways was an enormous task. Toward these goals, the Alaska District let contracts quickly. The first priorities were reopening highways and re-establishing essential water and fuel supplies. Talley, who had experience in military construction in Alaska during World War II, did much of the restoration design as a contractor with a private engineering firm. organized an emergency disaster team of 65 engineers from the Walla Walla, Seattle, and Portland districts to assist in the rebuilding program. Within the next few days Colonel Sawyer established special project offices at Anchorage, Valdez, and Seward to administer contracts for debris clearance, demolition, and repairs to sewers, water supplies, communications, and power distribution systems. Sawyer sent emergency teams in light aircraft to assess the damage. Less than 10 hours after the calamity, Alaska District Engineer Colonel Kenneth T. Though many of their homes were in ruins, employees of the Corps' Alaska District reported for duty immediately. The Corps of Engineers, in association with the Office of Emergency Planning (FEMA's predecessor), moved quickly to help communities in distress. Seward waterfront and railroad damage (left) Īnd tsunami damage along the waterfront at Kodiak (right) At Kodiak, a wave lifted the crab fishing fleet out of the harbor and carried boats through the town. Tidal waves also obliterated other ports along Alaska's southern coasts. Businesses on three blocks of 4th Avenue sank 10 to 20 feet into the earth.įormer six-story Four Seasons apartment building (left) Īnd Government Hill elementary school (right)Īt nearby Seward, which was preparing to celebrate its selection as an "All-American city," floods destroyed the industrial areas and the port, including the southern terminus of the Alaska Railroad. An elementary school and several homes slid into Ship Creek Valley, settling on top of an Alaska Railroad warehouse. In downtown Anchorage the upheaval leveled the unfinished Four Seasons apartment building and two parking garages. Property damage totaled more than $500 million. Only the low density of the state's population, and the hour-5:35 p.m., when schools were empty, business areas uncrowded, and tides low-prevented the death toll from exceeding 114.
The intensity of the shock measured between 8.4 and 8.6 on the Richter scale, releasing twice as much energy as the quake that destroyed San Francisco in 1906. On Good Friday afternoon, 27 March, a violent earthquake rocked 50,000 square miles of south-central Alaska. Army Corps of Engineers to the Alaskan earthquake of 1964 was prompt and positive.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
